PsiThera is redefining drug discovery for inflammation and immunology by integrating first-principles physics, predictive computation, experimental biophysics, mechanistic biology and human-in-the-loop design within a unified platform. We are able to identify and optimize oral small-molecule therapeutics for complex targets with exceptional efficiency.
Our approach brings together experienced drug hunters spanning the core domains of modern drug discovery: structural biophysics, mechanistic biology, medicinal chemistry and predictive algorithms to deliver best-in-class molecules for targets traditionally dominated by biologics. We leverage computational intelligence, where we fuse advanced physics, AI, and supercomputing power powered by humans in a closed-loop cycle to understand the mechanism of biological targets in atomistic detail and design novel oral medicines for challenging targets in our pipeline.
How we Discovery Oral Drugs for Inflammation and Immunology (I&I) Targets
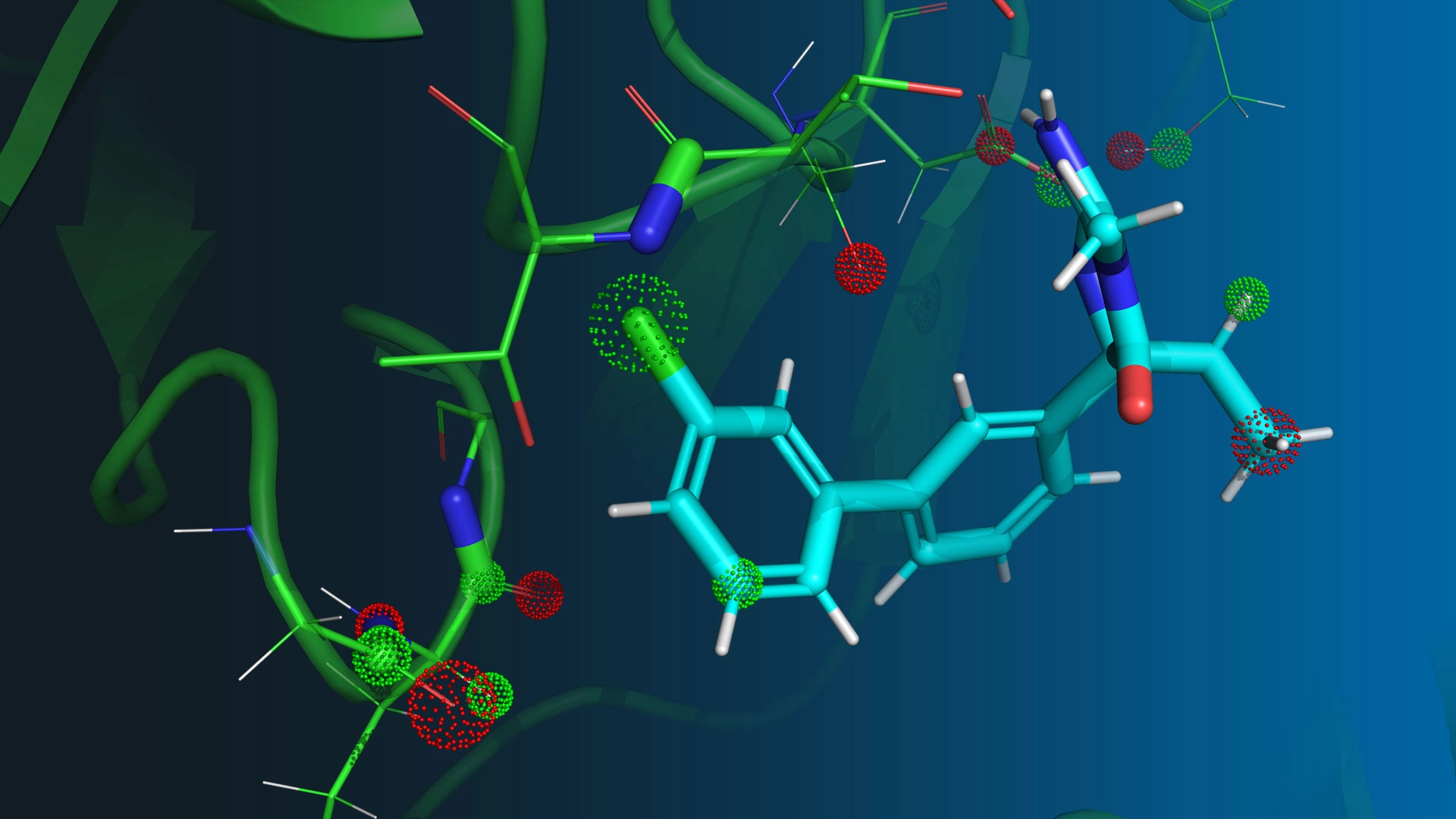
We start with protein targets that have strong biological and genetic validation, then model how those targets behave in their native environments rather than relying on static structures. Using the physics-native QUAISAR platform, we simulate biologically relevant protein motions to uncover cryptic pockets, transient states and druggable conformations that standard tools often miss. We integrate hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDX-MS), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), X-ray, cryogenic electron microscopy (Cryo-EM) data and mutagenesis and functional studies to constrain and refine these simulations, improving predictive accuracy and deepening mechanistic insight. We then develop bespoke biophysical and mechanistic biology assays to probe the pathway and validate the functional relevance of the conformational states we observe. These insights unlock opportunities for mechanistic differentiation from biologics leading to a more selective modulation of signaling pathways and, ultimately, to providing better options to patients.
Before exploring chemical space, our expert medicinal and computational chemists use our PsiVision data platform to interpret experimental and simulated data side-by-side, forming actionable design hypotheses that guide the next wave of bespoke chemical ideas. We then computationally generate and evaluate billions of synthetically tractable molecules based on project-specific objectives. We then use global and local machine learning models to filter for key absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME), safety and drug-like properties. Next, we triangulate with physics-based assays, including quantum chemistry calculations, free-energy simulations and molecular dynamics, to prioritize the most promising designs. Finally, we apply PsiVision to combine computed properties and experimental data with expert interpretation, enabling rapid and traceable decision-making. This process reduces billions of ideas to a few dozen molecules most likely to advance the project toward its target product profile (TPP).
Our in-house simulation engine, force fields, machine learning models and high-performance computing stack give us full control over the drug discovery process. We run long-timescale molecular dynamics on complete biological assemblies, including proteins, cofactors, membranes and ions. We perform hundreds of quantum mechanical calculations per ligand to parameterize accurate force fields. We scale workflows up or down based on project needs, from exploratory conformational sampling to high-throughput free-energy predictions. We integrate new data into models in real time, enabling human-in-the-loop learning that accelerates every design, predict, make, test, analyze (DPMTA) cycle. Because we own the entire technology stack, from physics to code to compute, we can adapt the platform rapidly to emerging biology.
PsiThera’s chemists, biophysicists, biologists, computational scientists and engineers work as one team to accelerate drug discovery. We design molecules using synthetic feasibility and building-block availability to ensure every concept can be made. Then we analyze biologically relevant protein motions (BRPM), free-energy landscapes and in vitro and in vivo pharmacology experiments together inside PsiVision, creating a unified view of data. The team makes rapid decisions based on the highest-value information rather than fixed cycles or opaque models. This integrated approach shortens timelines and increases the likelihood of success compared with traditional discovery workflows.
Motion-Based Drug Discovery: Powered by Physics, Accelerated by AI
Our QUAISAR (Quantum, AI and Structure-Activity Relationships) platform fuses advanced physics, AI, and supercomputing power to reveal the mechanism of biological targets in atomistic detail, allowing us to design novel medicines faster than traditional methods. We call this computational intelligence; the ability to reason about complex scientific problems, generate sophisticated hypotheses, make predictions grounded in reality and optimize drug candidates. By simulating protein motion with unprecedented realism and designing bespoke mechanistic assays in the lab, we design small molecules that precisely modulate immune pathways.